Published 15/11/2016
The responsible use of antibiotics is a key element of corporate responsibility for any company with farm animals in its supply chain. Neglect of this responsibility represents not only a gap in ethical practices but also a significant reputational risk.
The overuse of antibiotics in human medicine is partly responsible for the increase in antibiotic resistant bacteria. However, farm animal use contributes significantly, and for some infections it is the main source of resistance.
Producers routinely give farm animals – particularly pigs and poultry – preventative antibiotics to compensate for substandard living conditions where risk of disease runs high and to prevent infection when carrying out routine practices such as castration in pigs, and drying off lactating dairy cows.
This routine mass-medication of farm animals is contributing to the bacteria becoming resistant, making antibiotics increasingly ineffective for both animals and human alike.
A reduction in the routine use of antibiotics in livestock production requires an attitudinal shift towards more responsible use. Many companies are already addressing this by putting policies in place for regulating and reducing the prophylactic use of antibiotics.
Others, such as the British Poultry Council has set up an Antibiotic Stewardship Scheme to measure the usage of medicine in poultry meat flocks. Members of the BPC scheme do not support the routine use of antibiotics and have strict measures in place to ensure that where they are used, they are used responsibly and in line with the guidelines and principles outlined by the Responsible Use of Medicines in Agriculture Alliance (RUMA).
Compassion has been developing an Antibiotic Stewardship Programme (ASP) to encourage companies to adopt a roadmap for responsible antibiotic use. The roadmap provides a clear strategy for:
- Reducing the unnecessary use of antibiotics
- Eliminating/robustly regulating the use of human critical antibiotics
- Helping to prevent the development of antibiotic resistance
The roadmap recommends that companies develop a policy with clear aims and targets to achieve the responsible use of antibiotics, move to higher welfare farming systems where animals are kept healthy through improved living conditions and good husbandry practices, use more robust breeds which are less prone to infection, treat only sick animals with antibiotics and avoid using antibiotics that are ‘critically important’ to humans, such as cephalosporins and fluoroquinolones.
Based on scientific principles, best practice and experience of working with industry, Compassion has summarised a simple process for food businesses to follow, including four key pillars of activity, which are further detailed in the roadmap:
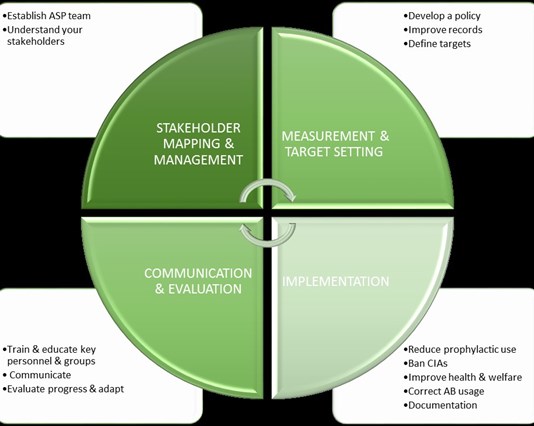
Implementing an effect Antibiotic Stewardship Programme (ASP) can bring many benefits: better animal health and welfare, closer relationships with your supply chain, and a positive story to tell to customers.
To find out more about Compassion’s roadmap, and how to develop an Antibiotic Stewardship Programme in your company, please contact the Food Business team.